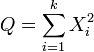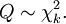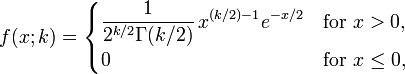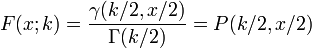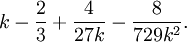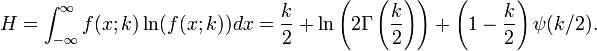Chi-squared distribution
About this schools Wikipedia selection
SOS Children made this Wikipedia selection alongside other schools resources. Do you want to know about sponsoring? See www.sponsorachild.org.uk
Probability density function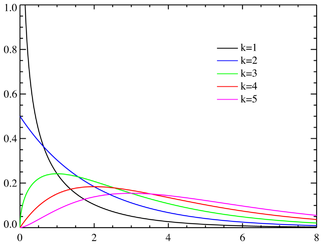 |
|
Cumulative distribution function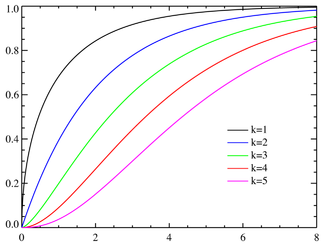 |
|
| Parameters | 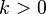 degrees of freedom degrees of freedom |
|---|---|
| Support | 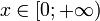 |
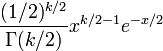 |
|
| CDF | 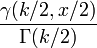 |
| Mean | 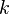 |
| Median | approximately 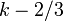 |
| Mode | 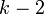 if if 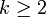 |
| Variance | 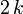 |
| Skewness | 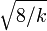 |
| Ex. kurtosis | 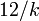 |
| Entropy | 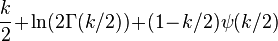 |
| MGF | 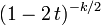 for for  |
| CF | 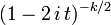 |
In probability theory and statistics, the chi-square distribution (also chi-squared or 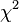 distribution) is one of the most widely used theoretical probability distributions in inferential statistics, e.g., in statistical significance tests. It is useful because, under reasonable assumptions, easily calculated quantities can be proven to have distributions that approximate to the chi-square distribution if the null hypothesis is true.
distribution) is one of the most widely used theoretical probability distributions in inferential statistics, e.g., in statistical significance tests. It is useful because, under reasonable assumptions, easily calculated quantities can be proven to have distributions that approximate to the chi-square distribution if the null hypothesis is true.
If 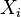 are k independent, normally distributed random variables with mean 0 and variance 1, then the random variable
are k independent, normally distributed random variables with mean 0 and variance 1, then the random variable
is distributed according to the chi-square distribution. This is usually written
The chi-square distribution has one parameter: 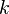 - a positive integer that specifies the number of degrees of freedom (i.e. the number of
- a positive integer that specifies the number of degrees of freedom (i.e. the number of 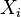 )
)
The chi-square distribution is a special case of the gamma distribution.
The best-known situations in which the chi-square distribution are used are the common chi-square tests for goodness of fit of an observed distribution to a theoretical one, and of the independence of two criteria of classification of qualitative data. However, many other statistical tests lead to a use of this distribution. One example is Friedman's analysis of variance by ranks.
Characteristics
Probability density function
A probability density function of the chi-square distribution is
where 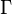 denotes the Gamma function, which takes particular values at the half-integers.
denotes the Gamma function, which takes particular values at the half-integers.
Cumulative distribution function
Its cumulative distribution function is:
where 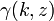 is the lower incomplete Gamma function and
is the lower incomplete Gamma function and 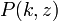 is the regularized Gamma function.
is the regularized Gamma function.
Tables of this distribution — usually in its cumulative form — are widely available and the function is included in many spreadsheets and all statistical packages.
Characteristic function
The characteristic function of the Chi-square distribution is
Properties
The chi-square distribution has numerous applications in inferential statistics, for instance in chi-square tests and in estimating variances. It enters the problem of estimating the mean of a normally distributed population and the problem of estimating the slope of a regression line via its role in Student's t-distribution. It enters all analysis of variance problems via its role in the F-distribution, which is the distribution of the ratio of two independent chi-squared random variables divided by their respective degrees of freedom.
Normal approximation
If 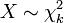 , then as
, then as 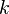 tends to infinity, the distribution of
tends to infinity, the distribution of 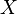 tends to normality. However, the tendency is slow (the skewness is
tends to normality. However, the tendency is slow (the skewness is 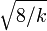 and the kurtosis excess is
and the kurtosis excess is 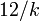 ) and two transformations are commonly considered, each of which approaches normality faster than
) and two transformations are commonly considered, each of which approaches normality faster than 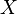 itself:
itself:
Fisher empirically showed that 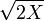 is approximately normally distributed with mean
is approximately normally distributed with mean 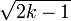 and unit variance. It is possible to arrive at the same normal approximation result by using moment matching. To see this, consider the mean and the variance of a Chi-distributed random variable
and unit variance. It is possible to arrive at the same normal approximation result by using moment matching. To see this, consider the mean and the variance of a Chi-distributed random variable 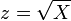 , which are given by
, which are given by  and
and 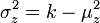 , where
, where 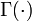 is the Gamma function. The particular ratio of the Gamma functions in
is the Gamma function. The particular ratio of the Gamma functions in 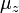 has the following series expansion :
has the following series expansion :
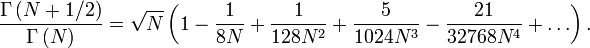 When
When 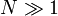 , this ratio can be approximated as follows:
, this ratio can be approximated as follows: 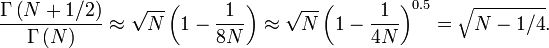
Then, simple moment matching results in the following approximation of 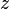 :
: 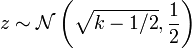 , from which it follows that
, from which it follows that 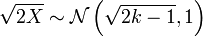 .
.
Wilson and Hilferty showed in 1931 that ![\sqrt[3]{X/k}](../../images/185/18595.png) is approximately normally distributed with mean
is approximately normally distributed with mean 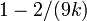 and variance
and variance 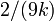 .
.
The expected value of a random variable having chi-square distribution with 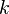 degrees of freedom is
degrees of freedom is 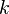 and the variance is
and the variance is 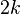 . The median is given approximately by
. The median is given approximately by
Note that 2 degrees of freedom lead to an exponential distribution.
Information entropy
The information entropy is given by
where  is the Digamma function.
is the Digamma function.
Related distributions
 is an exponential distribution if
is an exponential distribution if 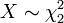 (with 2 degrees of freedom).
(with 2 degrees of freedom).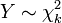 is a chi-square distribution if
is a chi-square distribution if  for
for 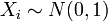 independent that are normally distributed.
independent that are normally distributed.- If the
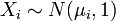 have nonzero means, then
have nonzero means, then  is drawn from a noncentral chi-square distribution.
is drawn from a noncentral chi-square distribution. - The chi-square distribution
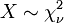 is a special case of the gamma distribution, in that
is a special case of the gamma distribution, in that 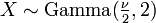 .
. 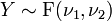 is an F-distribution if
is an F-distribution if 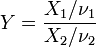 where
where 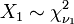 and
and 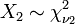 are independent with their respective degrees of freedom.
are independent with their respective degrees of freedom.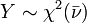 is a chi-square distribution if
is a chi-square distribution if 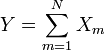 where
where 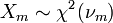 are independent and
are independent and 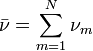 .
.- if
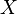 is chi-square distributed, then
is chi-square distributed, then 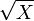 is chi distributed.
is chi distributed. - in particular, if
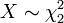 (chi-square with 2 degrees of freedom), then
(chi-square with 2 degrees of freedom), then 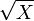 is Rayleigh distributed.
is Rayleigh distributed. - if
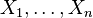 are i.i.d.
are i.i.d. 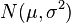 random variables, then
random variables, then 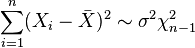 where
where 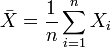 .
. - if
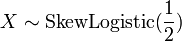 , then
, then 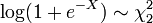
| Name | Statistic |
|---|---|
| chi-square distribution | 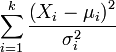 |
| noncentral chi-square distribution | 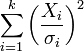 |
| chi distribution | 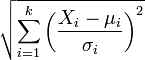 |
| noncentral chi distribution | 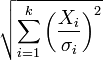 |